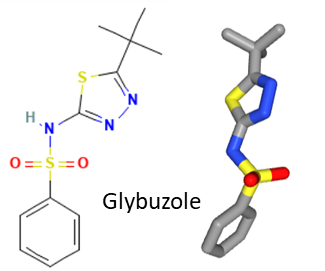
The oral drug Gludiase (1324 AN) was used essentially to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. The active principle of Gludiase was the benzene sulfonamide compound designated glybuzole or desaglybuzole. It is a thiadiazole derivative acting as a hypoglycemic agent. Glybuzole was used to lower blood glucose levels by increasing the release of insulin from pancreatic β-cells and stimulating insulin production. Upon binding to its receptor, the drug blocks ATP-dependent potassium channels, thereby stopping the flow of K+ ions into β-cells. The cell membrane becomes depolarized and calcium ions flow into the cells to cause the contraction of actomyosin filaments which are responsible for the exocytosis of insulin. Glybuzole belongs to a group of anti-hyperglycemic sulphonylureas. The drug has been widely used as an anti-diabetic drug in the 1970s but it was later replaced with more potent and safer products. A case of liver disease induced by glybuzole has been reported. The drug has been abandoned.