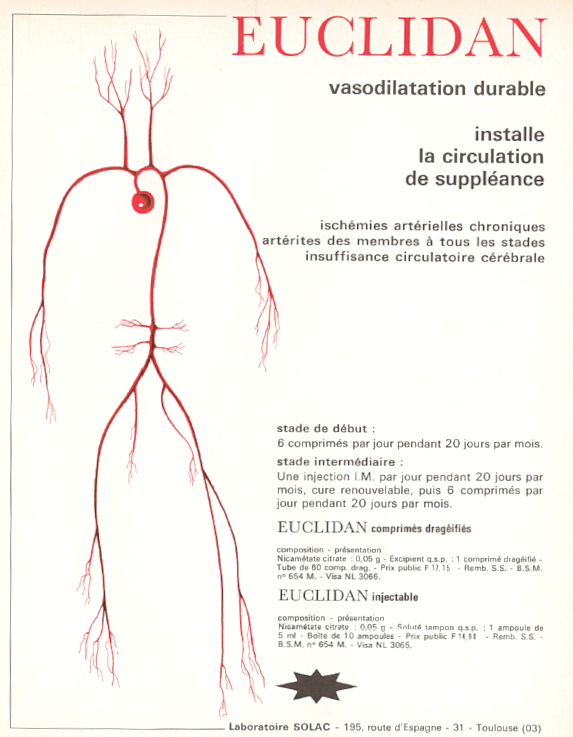
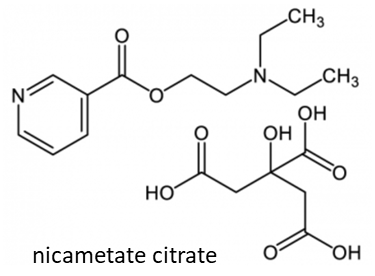
The active principle of Euclidan is a pyridine-carboxylate derivative called nicametate, an ester of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3, niacine). The drug was used to treat different types of vascular pathologies. Two drug forms have been developed: a solid form (coated tablets) and a liquid form (injectable i.m. product). Nicametate is a nicotinic ester of diethylaminoethanol initially developed in the early 1960s for the treatment of cerebral vascular disease. The drug was efficient at reducing the risk of cerebrovascular damages and death in patients diagnosed as ischemic stroke. The drug acted as a vasodilator, enhancing blood flow and oxygen to the brain, so as to aid stroke recovery. The product has been used also occasionally for treating intermittent claudication in certain patients. Euclidan is no longer used today. There are other therapeutic options to reduce the risk of vascular damages, notably with aspirin.
Categories: Gallery